Organizations go through certain stages of development as they mature. Much like individuals, they must go through these stages of evolution o2r they won’t have to tribal knowledge to help them understand why they do things a certain way.
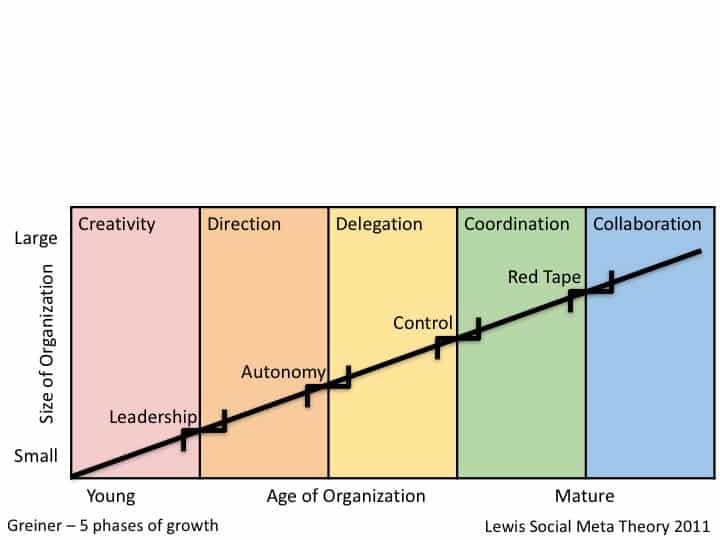
Figure a. (Greiner 1972) Evolution and Revolution as organizations grow
Creativity
The first stage new organizations take on is the creative stage. This is typically marked by a single leader with creative ideas. The leader changes direction of the organization rapidly responding to market and customer demands. Flexibility is the primary reason early stage companies survive. This stage is marked by a single leader making all the decisions without the need or time for input from others. Individuals in this type of organization are rewarded with equity participation so they are part of a bigger idea if it takes off.
The end of the creativity period begins with a crisis in Leadership.
Direction
Once the organization has figured out its market, it starts to become more efficient in how it manages its operations. Things that were performed manually are automated. These organizations still retain the strong leader, but they hire people to be managed.
Delegation
The third stage of the organization sees an emergence in the ability to expand the market originally identified in the first two stages. Market expansion does not require as much creativity, and the leader finds more like minded individuals who agree with their position. They are not interested in exploring all options for a decision, but are interested in people who agree with their position. Leaders in this stage will rarely seek out the opinion of others before making a decision. They are accustomed to being “right”. Rewards in the form of bonuses in a Delegation organization are based on personal achievement.
Coordination
Coordination refers to the organizations ability to work together to solve problems. The 4th stage of organizational evolution provides a framework for individuals to work together as groups interconnecting. Leaders delegate problem solving authority to individuals working in groups to solve. Coordination organizations reward individuals with profit sharing and stock options to encourage thinking about the organizations success and prevent departure from the organization.
Collaboration
Management focuses on problem solving and innovation through a matrix of teams. Leadership in these organizations are participative in that they seek all forms of input from various parts of the organization. Teams are rewarded with team bonuses instead of individual accomplishment bonuses. Collaboration organizations tend to outperform all other types of organizations.